MAN MEETS MACHINE: AUTONOMOUS DRIVING GETS THE HUMAN TOUCH AT CES 2020
Latest technology from NVIDIA DRIVE ecosystem shows more intuitive self-driving car experience.
Autonomous driving technology aims to eliminate the human at the wheel. However, the latest plans for the car of the future envision a greater integration of human-machine interaction throughout the rest of the vehicle.
At CES 2020, companies showed how they’re working toward safer and more efficient transportation. Drawing inspiration from creative concepts in other industries, and even trying out new areas of technological expertise, NVIDIA DRIVE partners showcased new ideas for human and machine harmony in the coming decade.
Quite a Concept
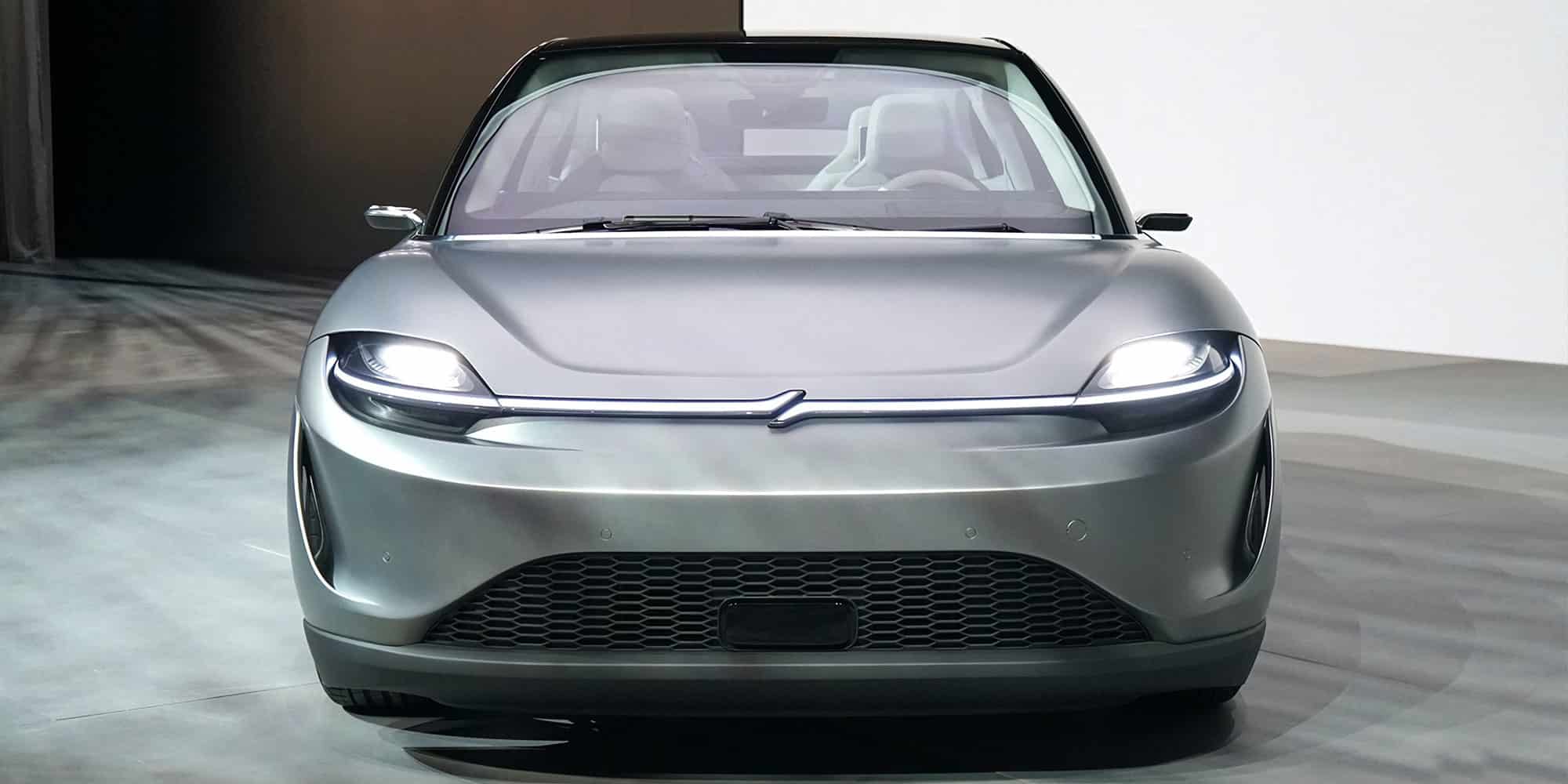
Drawing gearheads and technophiles alike, the Vision-S concept car was one of the most buzzed-about vehicles on the show floor. The electric vehicle incorporates cutting-edge imaging and sensor technology for autonomous driving as well as crystal-clear graphics for an intelligent cockpit experience. The most innovative feature of all? It wasn’t built by an automaker.
Electronics and entertainment company Sony worked with NVIDIA and other autotech companies to build its first ever vehicle prototype. Designed to showcase its latest sensor and AI infotainment technology, the sleek vehicle attracted crowds throughout the week.


The panoramic dashboard screen provides driving information, communication and entertainment, all effortlessly controlled by fluid gestures. Screens on the back of the front seats as well as speakers built into the headrests ensure every passenger can have a personalized experience.
The car’s hardware is designed for over-the-air updates, improving autonomous driving capabilities as well as adapting to the human driver and passengers’ preferences over time.
Though Sony isn’t building the Vision-S for production, the car’s concept for autonomy and seamless user experience provide a window into a highly intelligent transportation future.
Driving Instinct
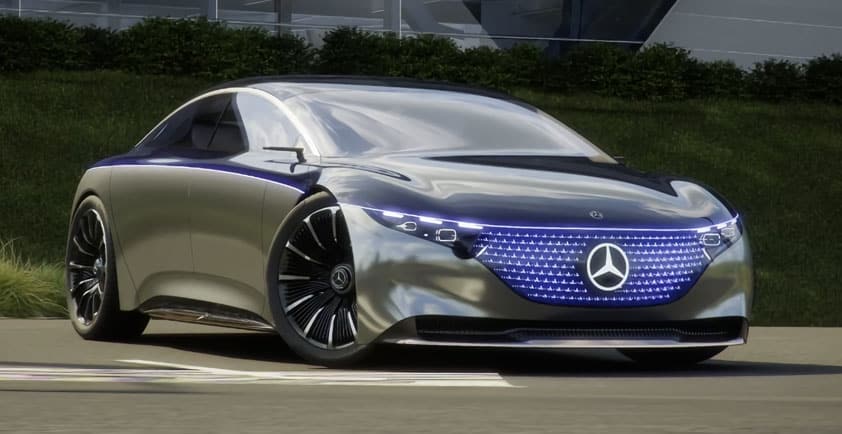
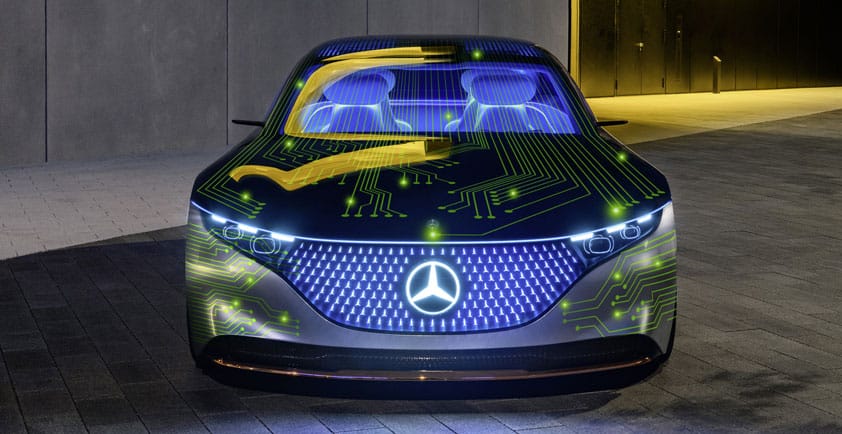
Mercedes-Benz, the automaker behind the first production AI cockpit, plans to take its revolutionary MBUX infotainment technology, powered by NVIDIA, even further.
During the CES opening keynote, Mercedes CEO Ola Kallenius said the next frontier for AI-powered infotainment is truly intuitive gesture control. The automaker’s vision for the future was then demonstrated in the Vision AVTR concept vehicle, designed for the upcoming sequels to the blockbuster film Avatar.
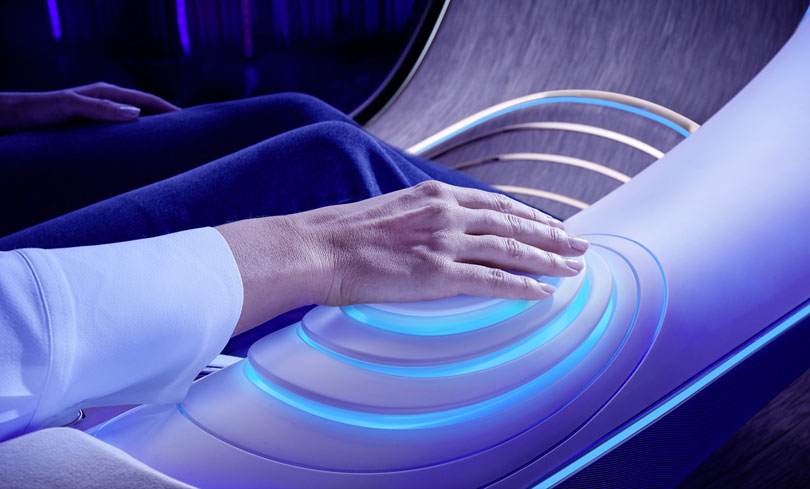
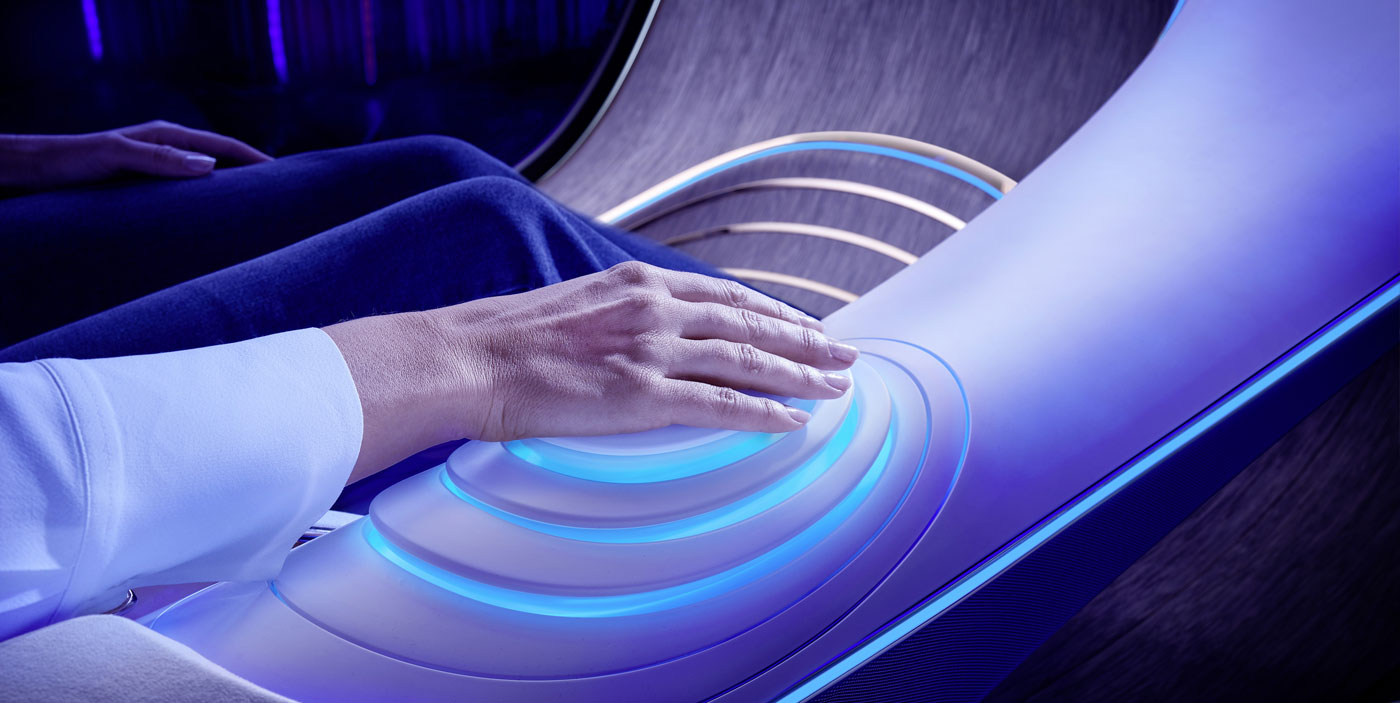


The hallmark feature of the Vision AVTR is the center console control element that replaces a typical steering wheel. It’s activated by human touch, using biometrics to control the car.
The concept illustrates Mercedes’ long-term vision of facilitating more natural interactions between the driver and the vehicle. And given the proliferation of the MBUX infotainment system — which is now in nearly 20 Mercedes models — this future may not be too far away.
AIs on the Road
CES attendees also experienced the latest innovations in autonomous driving firsthand from the NVIDIA DRIVE ecosystem.
Robotaxi company Yandex ferried conference goers around Las Vegas neighborhoods in a completely driverless ride. Powered by NVIDIA technology, the prototype vehicle reached speeds up to 45 miles per hour without any human intervention.
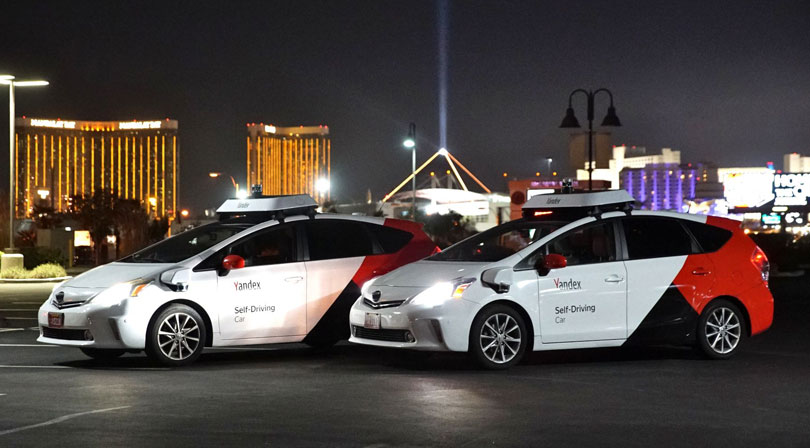
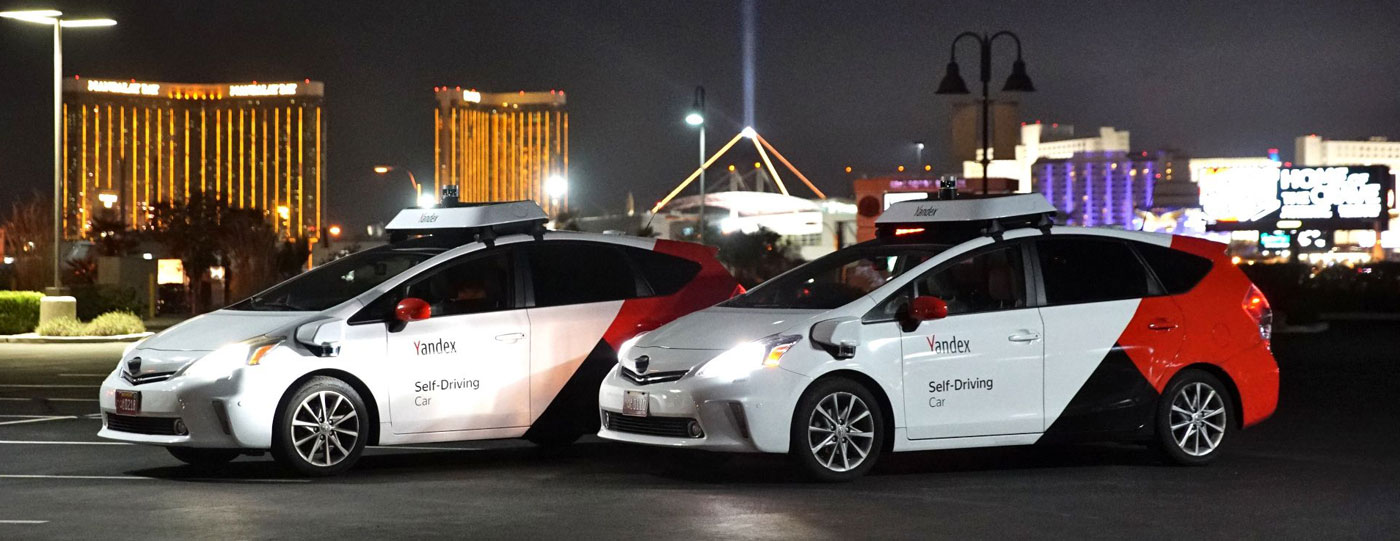


Yandex has been rapidly expanding in its mission to provide safe autonomous transportation to the public. Since last CES, the company has driven 1.5 million autonomous miles and provided more than 5,000 robotaxi rides with no human driver at the wheel.
Supplier Faurecia Clarion showed attendees how its working to alleviate the stress of parking with its autonomous valet system. Using the high-performance, energy-efficient DRIVE AGX platform, the advanced driver assistance system seamlessly navigated a parking lot.
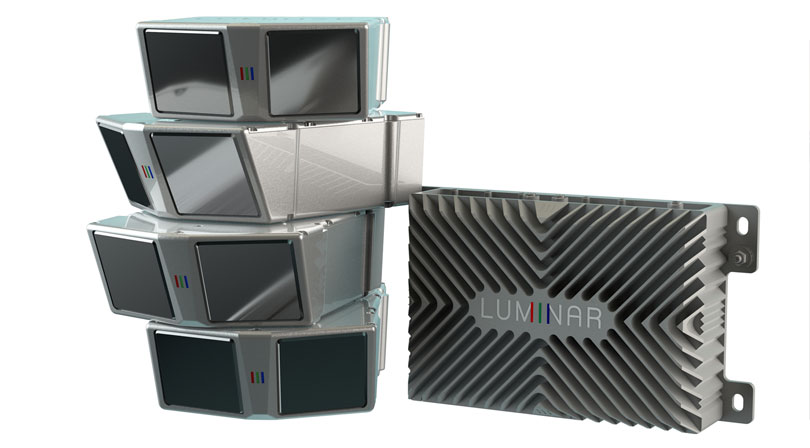
NVIDIA DRIVE ecosystem member Luminar brought the industry closer to widespread self-driving car deployment with the introduction of its Hydra lidar sensor. Designed for production Level 3 and Level 4 autonomous driving, the sensor is powered by NVIDIA Xavier and can detect and classify objects up to 250 meters away.


Analog Devices uses the NVIDIA DRIVE platform to help autonomous vehicles see and understand the world around them. The company demoed its imaging radar point cloud at CES, using NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier to process raw data from an imaging radar sensor into a perception point cloud.
With these latest developments in production technology as well as a cohesive vision for future AI-powered transportation, the age of self-driving is just a (human) touch away.
Author: Danny Shapiro - NVIDIA’s Senior Director of Automotive