INTEL 5G CONNECTED VEHICLES AND AUTONOMOUS DRIVING
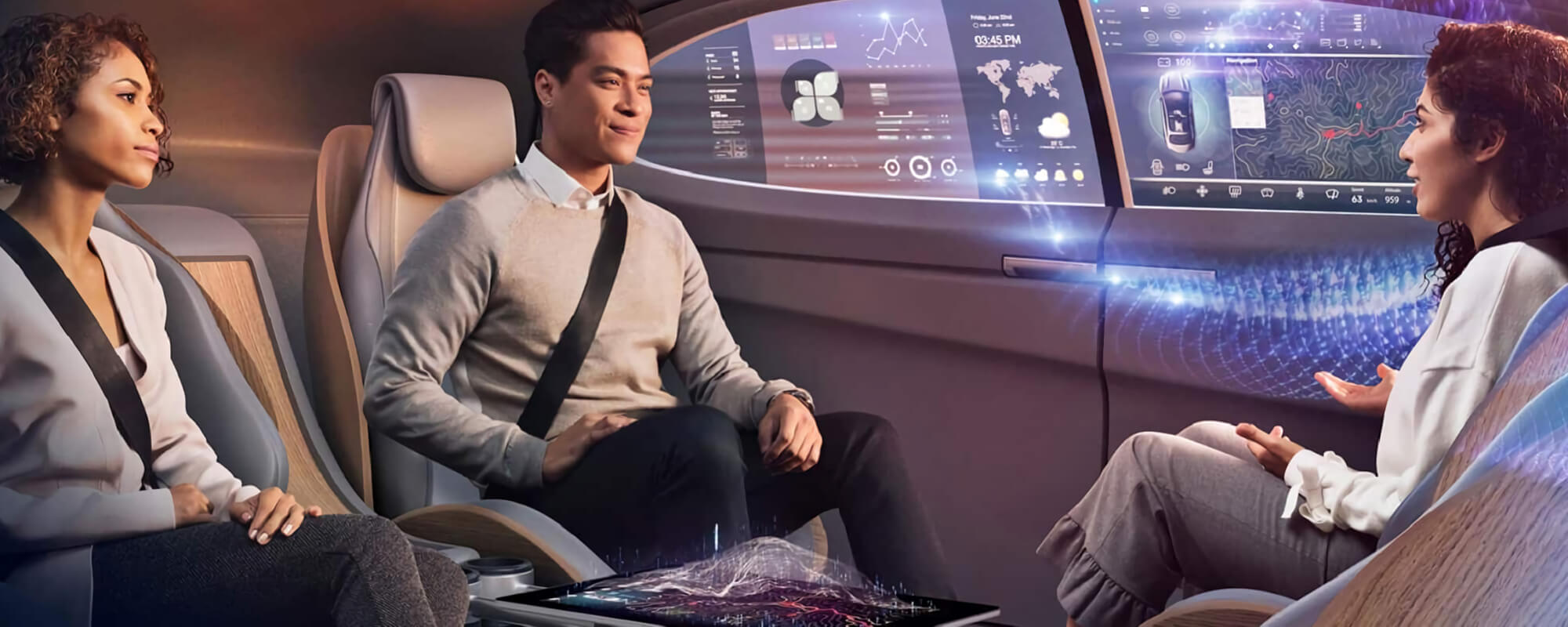
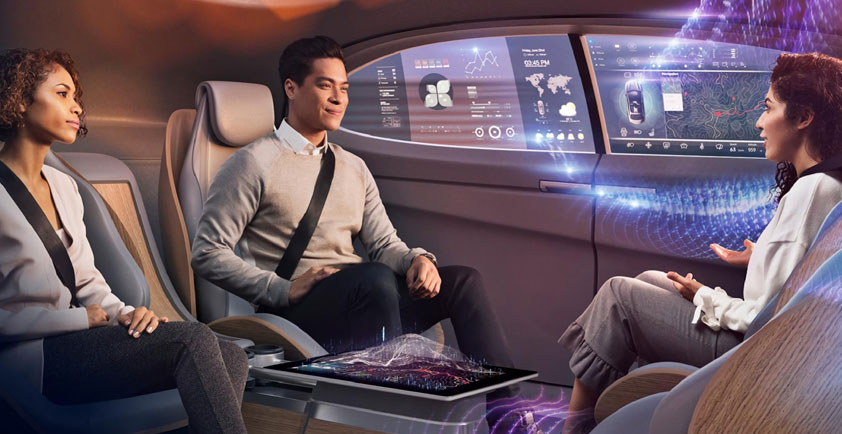
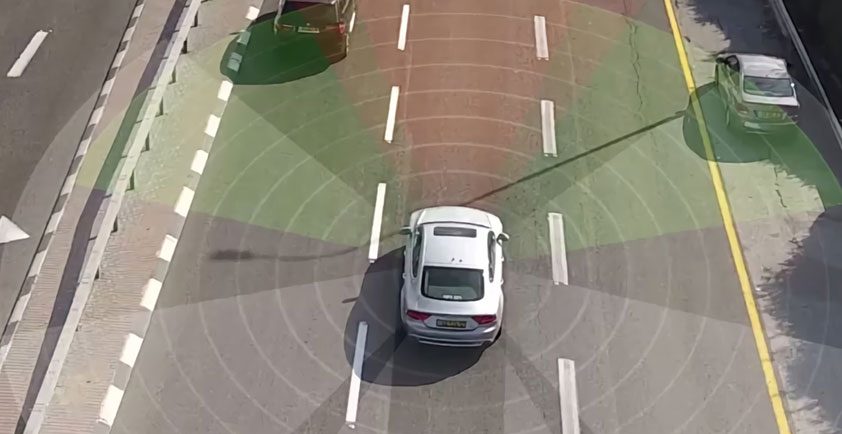
The automotive and transportation industries are experiencing a metamorphosis. Historically, vehicles have been isolated chunks of metal, with no ability to interact with each other or with the world around them. But a new vision is becoming reality: Connected vehicles and autonomous vehicles. At the core of this transformation is the 5G standard, with its low latency and higher bandwidth.
Connected cars have been in the works for a while, especially in the context of dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) and the Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) standard. So, what makes 5G so special?
“5G is a standard that goes beyond the mobile broadband. Its low latency, high throughput and the ability to do network slicing transforms the network to be much more cloud-like than a purposely built network focusing on mobile broadband or voice communication like we have in the past,” explains Caroline Chan, vice president of Intel’s 5G infrastructure team.
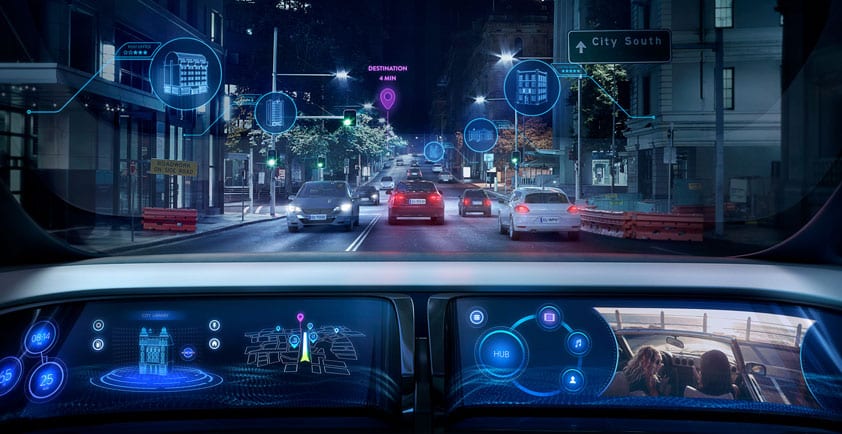
5G, combined with network function virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN), creates a far more flexible network that will affordably support many connected and autonomous vehicle capabilities that have previously been impractical. Use cases range from real-time high-definition maps and road hazard and closure updates to fleet tracking and infotainment. When you add in big data analytics, machine learning and artificial intelligence, you can begin to understand why Intel is so passionate about and interested in exploring this, together with the ecosystem.
Intel recently formed the Automotive Edge Computing Consortium (AECC), in conjunction with several other major industry players, to develop new architectures to support the expected 10 exabytes a month that will be generated from connected cars, with plans to also propose industry standards and best practices. McKinsey estimates that the overall revenue pool from car data monetization at a global scale might add up to USD 450 to 750 billion by 2030. Intel’s expertise in the cloud and data center can help create a flexible, agile network architecture that increases capacity and efficiency, and help service providers turn their cellular base stations into new revenue opportunities with innovations like edge computing and network slicing based on high-performance Intel® processors.
CONNECTED TRANSPORTATION USE CASES:
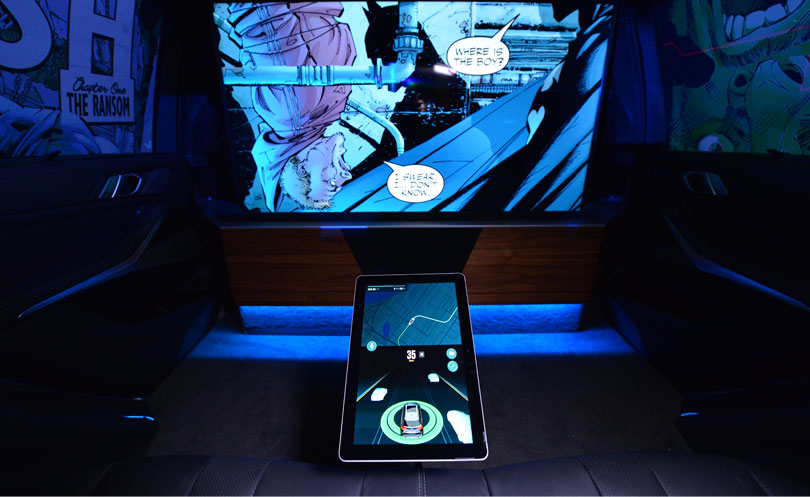


IMMERSIVE MEDIA
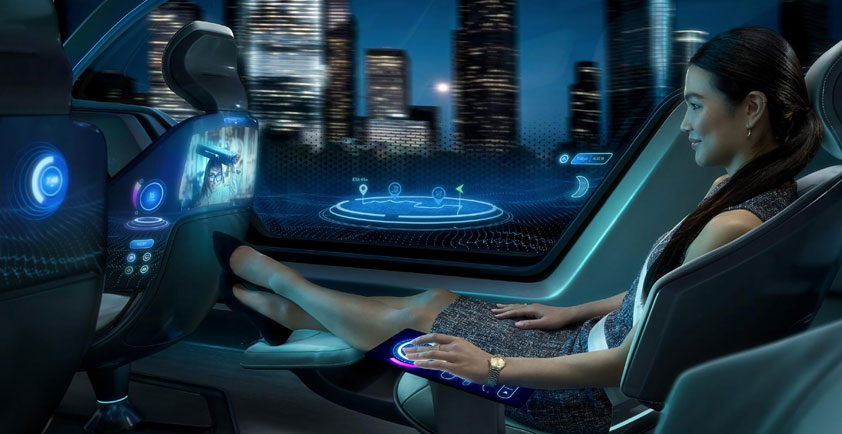
Amp Up Passenger Entertainment—5G networks with opportunistic device connectivity will enable passengers in autonomous vehicles to wirelessly stream a range of captivating new media as they travel to their destination. Two passengers could interact with movie characters in virtual reality while another competes in a cloud-based game at low-latency with high-end graphics and sound.
MOBILE VIDEOCONFERENCING
Turn Commute Time Into Productive Time—5G will deliver the high-bandwidth connectivity to empower passengers in autonomous vehicles to videoconference with the same level of quality and reliability as they would experience via a wired connection back at the office. Business professionals will be able to hold meetings, move work forward, and boost efficiency in transit to make the most of their time.
AUTONOMOUS SERVICES DELIVERY
Obtain Services On The Go—5G will equip autonomous vehicles, including drones, to conveniently bring goods and services to people, improving quality of life and presenting opportunities for businesses to offer alternate levels of service that can increase revenues. This transformation flips the typical purchase scenario, allowing people to easily incorporate shopping and errands into busy schedules. People can quickly order items and have them delivered while they are out having lunch, or even bring a clothing boutique right to their door, on demand.
AUTOMATED LOGISTICS
Streamline Business Operations—5G and Blockchain will proliferate a new generation of trucks, trains, ships, and more to improve delivery times and reduce costs. Digital shipping manifests will be transmitted wirelessly, and robotic cranes and forklifts will move shipping containers from ships onto nearby trains and trucks for inland distribution without the need for human control.